
Thermal imagers, also called thermal cameras, are heat sensors that pick up highly subtle temperature changes. The gadget takes in the scene’s infrared light and uses the data about the components’ temperature differences to generate an electronic picture.
More and more industries are finding uses for thermal imaging sensors. They offer a fast and accurate way to measure the heat energy and temperature emitted for various uses.
In manufacturing and emergency circumstances, thermal imaging cameras shine. Medical diagnostics has been further used in areas such as fixing broken things, studying buildings, managing the environment, and navigating alone.
Thermal Imaging Camera Definition
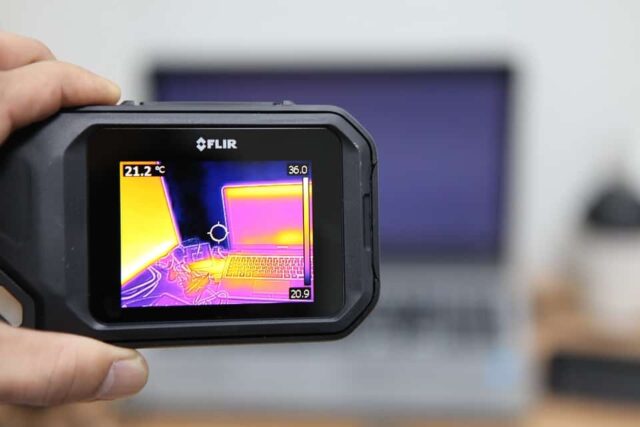
Thermographic cameras are handheld gadgets that can interpret heat signatures and display the data graphically or in color. This camera creates an image of the object’s temperature distribution from the infrared radiations emitted by the object.
The map’s various hues indicate where temperatures are low and high. Temperature hotspots are marked by red, yellow, and orange colors. Green denotes a comfortable temperature range (around that of a room’s temperature), while cooler hues of purple and blue are marked by their opposites. Images taken with an infrared camera, where temperatures are displayed in grayscale, allow a more detailed look.
The camera’s thermometer picks this up. Images captured by thermal imaging cameras might be utilized to identify and assess potential hazards. Investigations are conducted into the origins of excessive heat, hot spots, and insulation breaches.
The thermal imaging camera’s ability to detect and record invisible heat signatures to the naked eye is a significant advantage.
How the Infrared Cameras Work in Images Observations
A thermal imaging camera functions by capturing images in the infrared spectrum. In addition, they may “take a picture” or “thermograph” of the heat energy that objects emit. This is accomplished using a thermal imaging sensor and a customized camera lens.
Infrared light is converted into digital data by grids of pixels in pictures or heat sensors. The camera’s body converts the data into a temperature-based color map. We’ve provided a visual representation to make studying the color keyless a chore.
Key Specifications to Consider
Before making a purchase, here are some considerations for a thermal camera:
Resolution
The higher the resolution of an IR imaging camera’s detection, the more pixels it possesses. Picture processing and dynamic visual reconstruction are sped up with a lower spatial resolution number, while a wider field of view results from a more excellent resolution.
The thermal camera can focus on a target precisely thanks to its continual autofocus function. It has autofocussed capabilities, albeit sometimes manual adjustment is needed for the best results.
The Camera Autofocus

A constructed laser rangefinder enables the camera’s autofocus system to zero in on the subject after calculating its distance. The object is taken at various focal lengths, and the resulting photographs are blended in post-production to form a single, detailed image and high-resolution.
Lenses come in various types and sizes, including standard, telephoto, wide-angle, and macro. Pick a lens that satisfies your needs while capturing the scene you want in the finest resolution possible.
Color Scheme
With a suitable color scheme, you may draw attention to details in your design that would otherwise be lost. If you’re trying to draw attention to nuance, a monochromatic color scheme resembling amber or grayscale is a good choice.
Monochromatic colors like grayscale or amber help detect little shifts in temperature, but high-contrast color schemes are best for noticing apparent outliers.
Location markers and alarms of different colors alert you when temperatures rise or fall outside the normal range for the things you’re monitoring. Markers might be placed anywhere on the thermal image to denote a specific temperature.
Surfaces that deflect infrared light from other objects, like shiny metals, can cool those objects’ temperatures. The clarity of your IR image will decline due to this phenomenon. To achieve consistency and accuracy with your thermal photography, the settings on your equipment should be flexible.
Benefits of Thermal Imaging Cameras
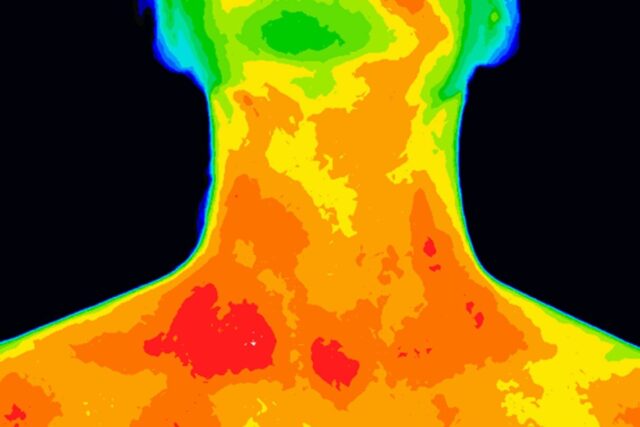
Thermal imaging cameras have an array of practical uses, ranging from industrial and environmental monitoring to use in the medical and automotive sectors. Thermal cameras provide great benefits for a variety of applications and industries—some that may not be so obvious. Here are just a few of the benefits of thermal imaging cameras:
- Non-Contact Detection: Thermal Cameras allow you to detect temperature even from a distance, by using infrared rays as opposed to contact sensors which require contact with the object or surface being monitored. This makes it easy for technicians in hazardous environments to perform their jobs safely without putting themselves at risk.
- Improved Remote Monitoring: Thermal Cameras can “see” temperatures over long distances, allowing you to monitor from far away without having to be physically present onsite. This makes it easier to manage large areas while still catching potential problems in real-time before they become serious issues.
- Quick Identification: Thermal Cameras allow technicians to quickly identify problems such as hotspots that could indicate dangerous electrical faults or a looming system failure that may need maintenance attention right away in order to prevent further damage or disruption of services.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: The near-instantaneous detection capabilities provided by thermal cameras allow technicians to accurately detect problems while they’re still relatively small so they can quickly take action instead of waiting until it becomes a major issue requiring an extended investigation and repair process that costs time and money in the long run.
- Reduce Risk: Certain misdiagnosed electrical issues can cause huge safety risks for both people and the product—meaning there could be a liability for those involved should something go wrong—but with accurate readings provided by thermal imaging systems, this risk is effectively minimized, if not eradicated entirely.
Summary
There are some components and systems that may only be visible with the aid of an infrared camera. They, too, are incredibly safe because of the remote nature of the process.
Thermographic imaging is a powerful tool for detecting problems in electrical, electronic, mechanical, and other industrial processes and mechanisms in real time. Recent technological advances have substantially enhanced infrared imaging, enabling its usage in a wider variety of industrial and commercial contexts at a lower price.













