If you are looking for online anonymity or a way to avoid those “geo-restricted blockers”, a proxy server is a great way to start. A proxy server is easy to use, fast and provides a good deal of anonymity. It acts as a middle-man between you and another service across the Internet.
In this article, we’ll define the technical definition of the proxy, and also show their popular types, use cases, and advantages and disadvantages.
So, What Is a Proxy?

A proxy is basically a server acting as an intermediary between two networks. The idea behind having this “intermediary” server is to create a structure in the traffic of complex and distributed networks.
A proxy server can centralize, organize, change, and clean requests and responses between a network requesting services (your computer) and a network providing the services (the Internet).
If you are behind a proxy, your computer on a local network and the Internet are divided by the proxy server. For example, if you are connected to an anonymous web proxy, the HTTPS requests coming from your computer will be masked by the proxy’s IP, and the proxy will forward the request to its destination.
Is a proxy server different from a VPN? A VPN and proxy are completely different technologies. One encrypts and builds up a network (VPN), and the other centralize messages (Proxy). But, there is a similarity between a VPN and proxy.
The fact that the VPN server is acting as a middle-man— an intermediary between the client (source) and web server (destination), makes the VPN server a kind of “trusted proxy”.
Why Do You Need a Proxy?

A proxy can be useful for a wide number of applications, such as, but not limited to:
- Accessing regional-locked content, like streaming or gaming services.
- Bypassing censorship set by the government.
- Avoiding network limits from corporate networks or schools.
- Avoid getting your IP blocked while web scraping.
- Fast and undetectable large-scale SEO campaigns with web scraping.
Types of Proxies
There are many types of proxies out there. But the most common being the protocol-based HTTP/HTTPS, and SOCKS proxies. These types of proxies can vary according to level of anonymity, IP source, and also its type of service.
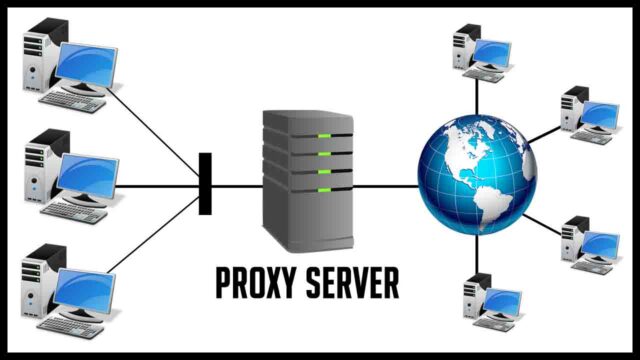
The screenshot below shows a simple diagram of a proxy forwarding traffic to the Internet. Without a proxy (red), access to specific portions of the Internet is blocked.
HTTP Proxy vs SOCKS Proxy

So what are the differences between the two most popular types of proxies? HTTP proxy vs SOCKs proxy?
An HTTP proxy (layer 7) is commonly used for anonymous web browsing. As mentioned in the beginning, proxies centralize requests. So when an HTTP proxy, centralizes HTTP, it is capable of changing the contents of the source HTTP request and re-route the request with the proxy’s IP.
That means when you are browsing the web, whatever is after the proxy, will see as if HTTP requests coming from the proxy, and not from you.
HTTP proxies only care about web-based traffic, but SOCKS (SOCKets Secure) doesn’t care about the type of application traffic going through. SOCKS work at the session layer (layer 5 of the OSI model) which opens, closes, and manages sessions between end-user application processes.
A SOCKS proxy allows you to filter any traffic, regardless of application. This is why SOCKS5 proxies are preferred for applications like torrenting and streaming. Now, SOCKS5, a new version of SOCKS, also integrates authentication for more security and is much faster.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Proxy Server

A proxy server adds an extra layer between you and an external server. Depending on how the anonymity level of that proxy server is configured, it can hide your IP or reveal it.
Additionally, depending on where the proxy server is deployed, such as behind your Internet gateway or across the world, the results will vary.
What Are the Pros of Using a Proxy?
- Bypass geo-restricted content – For example, if a proxy is located in the US, you should be able to access US-based content, like Netflix, HBO, Prime, etc.
- Get around web restrictions – If a local government or school has strict censorship or network restrictions, connecting to a proxy located in a different country or network will help bypass those regulations.
- Large-scale data scraping – Rotating proxies are highly efficient in terms of speed, keeping anonymity, and relatively cheap, which is great for data scraping.
- Controlling Internet usage – Offices use reverse proxies to control Internet usage inside corporate networks. A proxy may act as a firewall (but without the rules) to filter and block some traffic.
What Are the Cons of Using a Proxy?
- Free proxies are risky and slow – You never know the real intentions behind a free service provider. Free proxies could be logging your data and selling it, showing you lots of annoying ads, and even installing Bloatware, Malware, or crypto mining software.
- Proxies do not encrypt your traffic – A proxy will not encrypt data into code to conceal it from unauthorized access. If a packet sniffer is placed in the same network or in the traffic flow, anyone should be capable of looking into the contents of the data.
Recommendations When Using a Proxy?
Avoid using free proxies. Unless you are simply spoofing a location to browse without handling sensitive data— stay away from free proxies. Free proxies tend to attract lots of users.
So being full with other users sharing the same resources, makes the server 10x slower and a lot less safe. The risks are not only from the other users but also from the free proxy provider. Remember, proxies Do No Encrypt Data, they just mask the IP.
This is why it is not recommended to handle sensitive information while connected to public free proxies. If you really need to use a free proxy, use encryption yourself (SSL or HTTP) and avoid loading unknown JavaScript files.
Final Words
If you value privacy and speed, consider a private proxy. Private and paid proxies handle their servers and privacy in a completely different way. A clear distinction is that a private proxy allocates resources to the service itself.
These private proxy servers are not flooded by countless shared users, making them 10x faster. Plus, they have a privacy policy that clarifies how they are dealing with data logs. So, if privacy, speed, and customer service are important for you, a private proxy, such as, Rapidseebox can be the right choice.